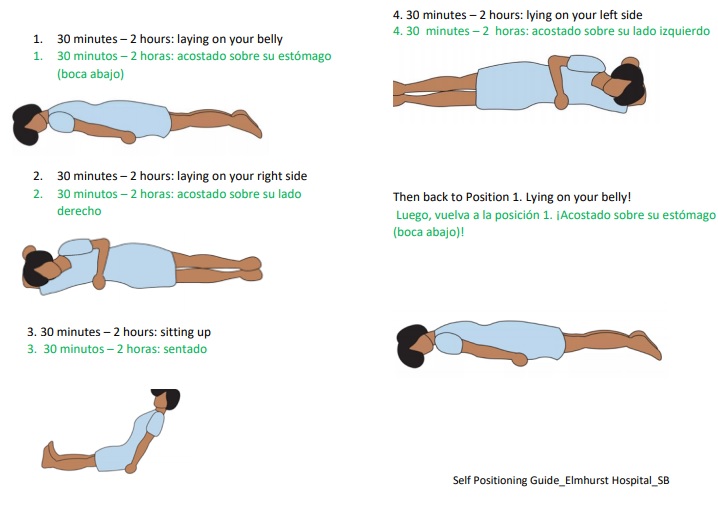
Prone bone meaning is a term that often confuses many people, as it relates to both anatomical positioning and specific bone conditions. Whether you're a student studying anatomy, a healthcare professional, or simply someone curious about human anatomy, understanding this concept can provide valuable insights. This article will delve deep into the meaning of prone bone and its implications in various contexts.
Positioning terms like "prone" and "supine" are essential in medical and anatomical studies. These terms help describe the orientation of the body and its parts, making communication in the healthcare field more precise. When we talk about prone bone meaning, we're discussing how bones are positioned and the potential conditions that arise from specific postures.
In this article, we will explore the concept of prone bone meaning, its anatomical significance, and its relevance in medical diagnostics. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of the term and how it applies in various scenarios.
Read also:Moneybagg Yo Height A Comprehensive Insight Into The Rappers Biography And Career
Table of Contents
- What is Prone Bone Meaning?
- Anatomy of Bones
- Prone Position Explained
- Common Prone Bone Conditions
- Prevention and Treatment
- Importance of Posture
- Prone Bone Meaning in Medical Contexts
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- References
What is Prone Bone Meaning?
Prone bone meaning refers to the positioning of bones when the body is in a prone position. The prone position is when an individual lies flat on their stomach, with the front of the body facing downward. In this posture, certain bones and joints experience pressure, which can lead to discomfort or even injury if maintained for prolonged periods.
Understanding the Term "Prone"
The term "prone" originates from the Latin word "pronus," meaning "bent forward" or "inclined." In medical terminology, it describes a position where the ventral side (front) of the body faces down. When discussing prone bone meaning, it's important to recognize how this position affects skeletal alignment and function.
For instance, lying in a prone position can place additional stress on the spine, hips, and shoulders. This stress may contribute to conditions such as osteoporosis, arthritis, or joint stiffness if not managed properly.
Anatomy of Bones
To fully grasp prone bone meaning, it's crucial to understand the basic anatomy of bones. The human skeleton consists of 206 bones, each serving a specific function in supporting the body, protecting vital organs, and enabling movement.
Key Components of the Skeletal System
- Skull: Protects the brain and supports the structures of the face.
- Spine: Provides structural support and houses the spinal cord.
- Ribcage: Shields the heart and lungs.
- Limbs: Facilitates movement and manipulation of the environment.
Each bone is made up of compact and spongy bone tissue, covered by a layer called the periosteum. Understanding these components helps in diagnosing and treating conditions related to prone bone positioning.
Prone Position Explained
The prone position is widely used in medical and therapeutic settings. It is often employed during surgeries, physical therapy, and diagnostic procedures like MRI scans. However, maintaining this position for extended periods can have adverse effects on bone health.
Read also:Scarlett Johansson Before And After Breast Reduction A Comprehensive Look
Advantages of the Prone Position
Despite its potential drawbacks, the prone position offers several benefits:
- Improves ventilation in certain lung conditions.
- Facilitates access to the back during surgical procedures.
- Reduces pressure on the abdomen in some cases.
Understanding these advantages can help healthcare providers make informed decisions about when to use the prone position.
Common Prone Bone Conditions
Prolonged exposure to the prone position can lead to various bone-related conditions. Some of the most common include:
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. The prone position can exacerbate this condition by placing undue stress on weight-bearing bones.
Arthritis
Arthritis involves inflammation of the joints, causing pain and stiffness. Lying in a prone position for extended periods can worsen symptoms, particularly in the spine and hips.
Joint Stiffness
Joint stiffness is a common complaint among individuals who spend long hours in the prone position. This condition can limit mobility and affect daily activities.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing and treating prone bone conditions requires a multifaceted approach. Here are some strategies to consider:
Preventive Measures
- Maintain proper posture during daily activities.
- Engage in regular exercise to strengthen bones and muscles.
- Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.
Treatment Options
Treatment for prone bone conditions may include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Importance of Posture
Posture plays a critical role in bone health. Maintaining good posture helps distribute weight evenly across the skeleton, reducing the risk of injury and discomfort. Whether sitting, standing, or lying down, proper alignment is essential for preventing prone bone conditions.
Tips for Maintaining Good Posture
- Keep your shoulders back and relaxed.
- Align your ears, shoulders, and hips in a straight line.
- Avoid slouching or hunching forward.
By following these tips, you can protect your bones and joints from the adverse effects of poor posture.
Prone Bone Meaning in Medical Contexts
In medical settings, prone bone meaning takes on added significance. Healthcare providers use this term to describe the impact of prone positioning on bone health and function. Understanding this concept can lead to better patient outcomes and more effective treatment plans.
Applications in Surgery
During surgical procedures, the prone position is often used to access specific areas of the body. However, surgeons must be mindful of the potential risks to bone health and take steps to minimize these risks.
For example, using padded supports and adjusting the patient's position frequently can help prevent pressure sores and joint stiffness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between prone and supine positions?
The prone position involves lying face down, while the supine position involves lying face up. Both positions have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the context in which they are used.
Can prolonged prone positioning cause permanent damage to bones?
In some cases, prolonged prone positioning can lead to permanent damage, particularly in individuals with pre-existing bone conditions. However, with proper precautions and interventions, this risk can be minimized.
How can I improve my bone health?
To improve bone health, focus on a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engage in regular weight-bearing exercise, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Conclusion
Prone bone meaning is a critical concept in understanding the relationship between body positioning and bone health. By exploring the anatomy of bones, the implications of the prone position, and common bone conditions, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this topic.
We encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. Additionally, feel free to leave comments or questions below. For more insights into bone health and related topics, explore our other articles on the website.
References
1. National Institutes of Health. (2022). Bone Health. Retrieved from [NIH Website].
2. World Health Organization. (2021). Posture and Bone Health. Retrieved from [WHO Website].
3. Mayo Clinic. (2023). Prone Position in Medical Settings. Retrieved from [Mayo Clinic Website].