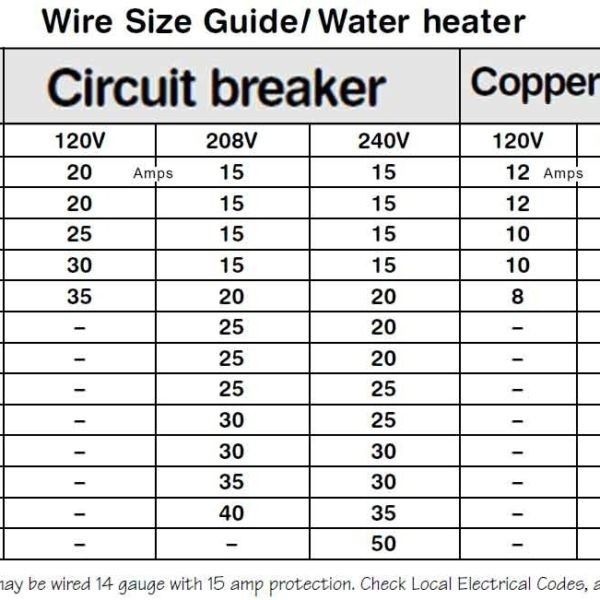
When it comes to electrical wiring, knowing the right wire size is crucial for safety and efficiency. The 10 amp wire size, commonly referred to as 10 AWG (American Wire Gauge), plays a significant role in various electrical applications. Understanding its specifications, uses, and limitations is essential for anyone working with electrical systems.
Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a professional electrician, having the correct knowledge about 10 AWG wire size can prevent electrical hazards and ensure optimal performance. This article will delve into everything you need to know about 10 AWG wire, including its applications, current-carrying capacity, and installation considerations.
Our aim is to provide you with a detailed and reliable guide that adheres to the highest standards of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of 10 AWG wire and how to use it effectively in your projects.
Read also:Judith Barsi Brother Unveiling The Forgotten Story
Table of Contents
- Introduction to 10 AWG Wire
- Understanding the Wire Gauge System
- Current-Carrying Capacity of 10 AWG Wire
- Applications of 10 AWG Wire
- Installation Tips for 10 AWG Wire
- Variations of 10 AWG Wire
- Comparison with Other Wire Sizes
- Safety Considerations
- Common Questions About 10 AWG Wire
- Conclusion
Introduction to 10 AWG Wire
What is 10 AWG Wire?
The 10 AWG wire, or 10 American Wire Gauge, is a standard wire size used in electrical installations. It is commonly used for circuits that carry a current of up to 30 amps at 75°C. This wire size is particularly suitable for residential and commercial applications where moderate current loads are required.
10 AWG wire is made from either copper or aluminum, with copper being the preferred choice due to its superior conductivity and durability. The wire is available in both solid and stranded forms, each having its own advantages depending on the application.
Understanding the Wire Gauge System
The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is a standardized system used to specify the diameter of round, solid, and cylindrical electrical conductors. The gauge number indicates the wire's thickness, with lower numbers representing thicker wires. For example, 10 AWG wire is thicker than 12 AWG but thinner than 8 AWG.
Understanding the wire gauge system is essential for selecting the appropriate wire size for your electrical needs. Factors such as current load, voltage drop, and ambient temperature must be considered when choosing the right wire gauge.
Current-Carrying Capacity of 10 AWG Wire
Maximum Current Load
The 10 AWG wire is designed to handle a maximum current load of up to 30 amps at 75°C. However, it's important to note that the actual current-carrying capacity can vary based on factors such as insulation type, ambient temperature, and wire length. For instance, wires in high-temperature environments may need to be derated to ensure safe operation.
- At 60°C: Maximum current load is approximately 20 amps.
- At 75°C: Maximum current load is approximately 30 amps.
- At 90°C: Maximum current load is approximately 35 amps.
Applications of 10 AWG Wire
10 AWG wire is widely used in various electrical applications, including:
Read also:Comprehensive Guide To Prenatal Supplements Ensuring A Healthy Pregnancy
- Residential wiring for 240-volt circuits, such as water heaters and air conditioners.
- Commercial installations for lighting and power distribution.
- Automotive applications, such as wiring for trailers and RVs.
- Solar power systems for connecting solar panels to inverters.
Installation Tips for 10 AWG Wire
Best Practices
Proper installation of 10 AWG wire is critical for ensuring safety and efficiency. Here are some tips to follow:
- Use the correct tools for stripping and crimping the wire.
- Ensure all connections are secure and properly insulated.
- Follow local electrical codes and regulations.
- Consider the wire's length and voltage drop when planning your installation.
Variations of 10 AWG Wire
Solid vs. Stranded Wire
10 AWG wire is available in both solid and stranded forms. Solid wire consists of a single conductor and is ideal for fixed installations where flexibility is not required. Stranded wire, on the other hand, consists of multiple thin wires twisted together, making it more flexible and suitable for applications where movement is necessary.
Comparison with Other Wire Sizes
Choosing the right wire size depends on the specific requirements of your project. Here's a comparison of 10 AWG wire with other common wire sizes:
- 8 AWG: Larger diameter, suitable for higher current loads.
- 12 AWG: Smaller diameter, suitable for lower current loads.
- 14 AWG: Even smaller diameter, commonly used for light-duty applications.
Safety Considerations
Avoiding Electrical Hazards
Safety should always be a top priority when working with electrical wiring. Here are some safety considerations to keep in mind:
- Always turn off the power before working on electrical circuits.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Ensure all connections are tight and secure to prevent overheating.
- Regularly inspect wires for signs of damage or wear.
Common Questions About 10 AWG Wire
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about 10 AWG wire:
- Can 10 AWG wire handle 40 amps? No, 10 AWG wire is rated for a maximum of 30 amps at 75°C. Using it for higher loads can cause overheating and potential hazards.
- What is the voltage drop for 10 AWG wire? Voltage drop depends on the wire length and current load. It's important to calculate voltage drop to ensure proper performance.
- Is 10 AWG wire suitable for outdoor use? Yes, as long as it is properly insulated and rated for outdoor applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the 10 AWG wire size is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. From its current-carrying capacity to its various applications, this wire plays a vital role in ensuring safe and efficient electrical installations.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more in-depth guides on electrical wiring and related topics.
Data Source: National Electrical Code (NEC) and IEEE standards.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/electrical-wire-sizes-1152851-1c278609d8364a7e93e277903520836e.png?strip=all)