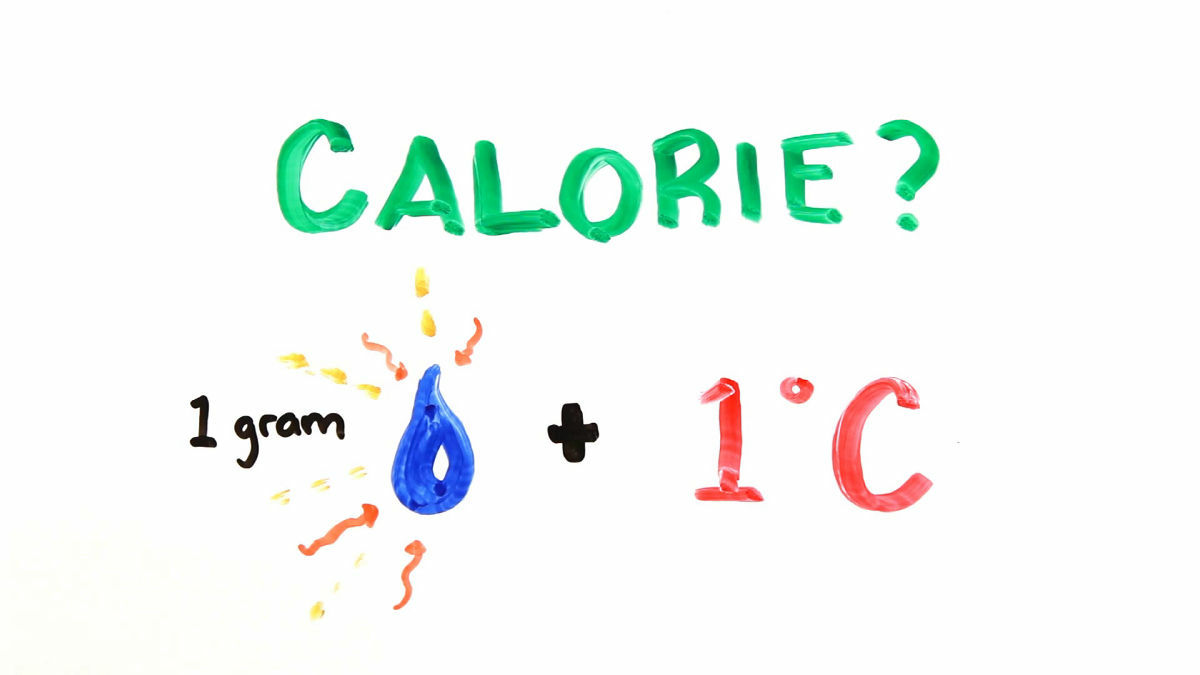Calories play a critical role in our daily lives, yet many people are still unclear about what kcal truly means and how it affects our health. The term "kcal" stands for kilocalories, which is the unit used to measure the energy content in food. Whether you're trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, understanding kcal is essential for achieving your goals.
From nutrition labels to fitness apps, kcal is a term we encounter frequently. However, it's not just about counting numbers; it's about understanding how our bodies use energy and how different foods contribute to our overall health. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of kcal, its importance, and how you can use this knowledge to improve your well-being.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of kcal and its role in your diet. Let's get started!
Read also:Atl 2 Release Date The Highly Anticipated Sequel Youve Been Waiting For
Table of Contents
- What is kcal?
- How kcal Represents Biological Energy
- Understanding Calories in Food
- Determining Your Daily Caloric Needs
- The Relationship Between Calories and Weight
- How to Burn Calories Effectively
- Reading Nutrition Labels for kcal
- Common Myths About kcal
- Health Implications of kcal Intake
- Conclusion: Putting kcal Knowledge into Practice
What is kcal?
The term "kcal" refers to kilocalories, which is the scientific unit used to measure the energy content in food. One kilocalorie equals 1,000 calories, making it a more practical unit for measuring the energy we consume and expend. Essentially, kcal tells us how much energy is stored in the food we eat and how much energy our bodies need to function.
Understanding kcal is crucial because it directly impacts our health and well-being. Whether you're an athlete looking to optimize performance or someone trying to manage your weight, kcal provides a quantifiable way to track your energy intake and expenditure.
Why is kcal Important?
- It helps in planning balanced diets.
- It aids in weight management by tracking energy balance.
- It ensures adequate energy intake for bodily functions.
How kcal Represents Biological Energy
At its core, kcal represents the energy required to sustain life. Our bodies rely on kcal to perform basic functions such as breathing, digestion, and movement. This energy comes from the macronutrients in our diet—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—which are broken down during digestion and converted into usable energy.
For example, carbohydrates provide 4 kcal per gram, proteins also provide 4 kcal per gram, and fats provide a higher 9 kcal per gram. Understanding the kcal content of these macronutrients helps in creating a balanced diet tailored to individual needs.
Energy Conversion in the Body
When we consume food, our bodies metabolize the nutrients and convert them into energy. This energy is then used to fuel various physiological processes, including:
- Basal metabolic rate (BMR): The energy required for basic bodily functions at rest.
- Physical activity: The energy expended during exercise and daily activities.
- Thermic effect of food (TEF): The energy used to digest and process food.
Understanding Calories in Food
Calories in food are measured in kcal, and this measurement is critical for maintaining a healthy diet. Foods with high kcal content, such as fatty or sugary items, provide more energy but can lead to weight gain if consumed in excess. Conversely, foods with lower kcal content, like fruits and vegetables, are essential for providing nutrients without excessive energy intake.
Read also:Catriona Gray Split The Untold Story Behind The Controversy
It's important to note that not all kcal are created equal. The quality of the food you consume plays a significant role in your overall health. For instance, 100 kcal from a piece of fruit will provide more nutrients and fiber than 100 kcal from a candy bar.
Key Sources of kcal in Your Diet
- Fruits and vegetables: Low kcal but high in vitamins and minerals.
- Whole grains: Provide complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
- Lean proteins: Essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Healthy fats: Support brain function and hormone production.
Determining Your Daily Caloric Needs
Calculating your daily caloric needs involves several factors, including age, gender, weight, height, and activity level. The Harris-Benedict equation and the Mifflin-St Jeor equation are two popular methods used to estimate basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is then adjusted based on physical activity levels to determine total daily energy expenditure (TDEE).
For example, a sedentary individual may require around 1,600-2,000 kcal per day, while an active person might need 2,400-3,000 kcal or more. Understanding your unique caloric needs allows you to create a personalized nutrition plan that supports your goals.
Factors Affecting kcal Requirements
- Age: Metabolism slows with age, reducing kcal needs.
- Gender: Men typically require more kcal than women due to higher muscle mass.
- Activity level: Physical activity increases kcal expenditure.
The Relationship Between Calories and Weight
The relationship between kcal and weight is based on the principle of energy balance. If you consume more kcal than your body burns, the excess energy is stored as fat, leading to weight gain. Conversely, consuming fewer kcal than your body needs results in weight loss as stored fat is used for energy.
Maintaining a balanced diet and regular physical activity are key to achieving and sustaining a healthy weight. It's important to focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide essential vitamins and minerals while managing kcal intake.
Strategies for Weight Management
- Track your kcal intake using apps or food diaries.
- Incorporate regular exercise into your routine.
- Choose whole, unprocessed foods over processed alternatives.
How to Burn Calories Effectively
Burning kcal effectively requires a combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and lifestyle changes. Cardiovascular activities like running, cycling, and swimming are excellent for burning kcal quickly, while strength training builds muscle, which increases your resting metabolic rate.
In addition to formal exercise, incorporating small changes into your daily routine can also help burn kcal. For instance, taking the stairs instead of the elevator or walking during breaks can contribute to your overall energy expenditure.
Effective kcal-Burning Activities
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): Burns kcal efficiently in a short time.
- Walking: A low-impact activity that can burn 100-300 kcal per hour.
- Strength training: Builds muscle and boosts metabolism.
Reading Nutrition Labels for kcal
Nutrition labels are a valuable tool for understanding the kcal content of the foods you consume. These labels provide detailed information about serving sizes, kcal per serving, and macronutrient breakdown. By reading and interpreting nutrition labels, you can make informed decisions about your diet.
For example, a food item labeled as having 200 kcal per serving may seem reasonable, but if the package contains multiple servings, you could easily consume double that amount without realizing it. Always pay attention to serving sizes and portion control.
Tips for Reading Nutrition Labels
- Check the serving size and adjust kcal accordingly.
- Look for the kcal content per serving, not per package.
- Consider the macronutrient breakdown for balanced nutrition.
Common Myths About kcal
There are several misconceptions surrounding kcal that can lead to confusion and ineffective dieting strategies. One common myth is that all kcal are equal, which ignores the importance of nutrient quality. Another myth is that skipping meals is an effective way to reduce kcal intake, when in fact it can slow down your metabolism and lead to overeating later.
By dispelling these myths and focusing on evidence-based nutrition, you can make better choices for your health.
Debunking kcal Myths
- Not all kcal are equal; nutrient quality matters.
- Skipping meals can harm your metabolism and lead to weight gain.
- Low-fat or fat-free foods are not always healthier options.
Health Implications of kcal Intake
Excessive kcal intake can lead to obesity, which is a risk factor for numerous health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. On the other hand, insufficient kcal intake can result in malnutrition, fatigue, and weakened immune function. Striking the right balance is essential for maintaining long-term health.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help you develop a nutrition plan that meets your specific needs and goals. They can provide guidance on appropriate kcal intake based on your age, activity level, and health status.
Long-Term Health Benefits of Balanced kcal Intake
- Improved energy levels and mental clarity.
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- Enhanced overall well-being and quality of life.
Conclusion: Putting kcal Knowledge into Practice
In conclusion, understanding the meaning of kcal and its role in your diet is essential for achieving optimal health. By calculating your daily caloric needs, reading nutrition labels, and incorporating regular physical activity, you can create a balanced lifestyle that supports your goals.
We encourage you to take action by tracking your kcal intake, experimenting with new recipes, and sharing this article with others who may benefit from the information. Your journey to better health starts with knowledge, and kcal is a key piece of the puzzle. Don't forget to leave a comment below or explore other articles on our site for more tips and insights!
References:
- World Health Organization (WHO). (2022). Healthy diet. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/healthy-diet
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2023). Calories. Retrieved from https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/calories/