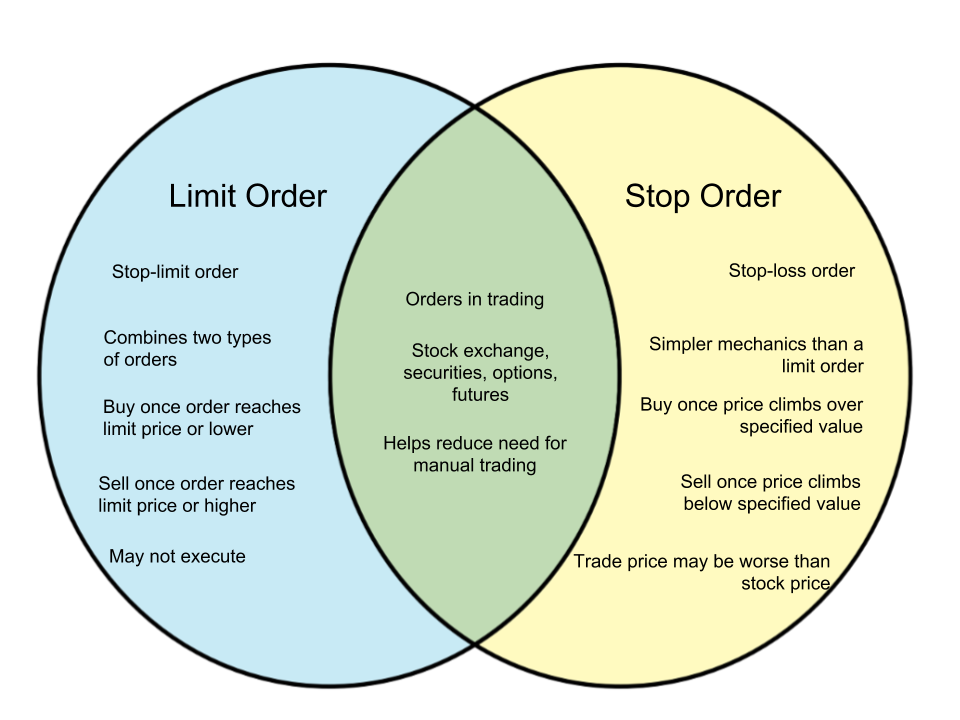
Stop limit order is a powerful trading tool that allows investors to specify both the price at which they want their order to activate and the price range within which the trade should be executed. This type of order gives traders more control over their transactions and helps protect them from sudden price fluctuations. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding how stop limit orders work can significantly enhance your trading strategy.
In today's fast-paced financial markets, having precise control over your trades is crucial. Stop limit orders provide traders with the ability to set boundaries for their transactions, ensuring that they only execute under specific conditions. This feature makes them particularly useful for protecting profits and minimizing losses in volatile markets.
This article will delve into the intricacies of stop limit orders, explaining their mechanics, benefits, and potential drawbacks. We'll also explore real-world examples and expert tips to help you implement this strategy effectively in your trading activities. Let's dive in!
Read also:Mariah The Scientist Ello Exploring The Fascinating World Of A Visionary Mind
Table of Contents
- What is Stop Limit Order?
- How Does Stop Limit Order Work?
- Advantages of Stop Limit Order
- Disadvantages of Stop Limit Order
- When to Use Stop Limit Order
- Examples of Stop Limit Order in Action
- Stop Limit Order vs Stop Market Order
- Common Mistakes to Avoid with Stop Limit Orders
- Best Practices for Traders Using Stop Limit Orders
- Conclusion
What is Stop Limit Order?
A stop limit order is a type of trade order that combines the features of both stop orders and limit orders. It consists of two price points: the stop price and the limit price. When the market price reaches the stop price, the order becomes active and turns into a limit order. The limit order will then be executed at the specified limit price or better.
This order type offers traders greater precision and control over their trades. By setting a stop price, traders can trigger the order when the market reaches a certain level, while the limit price ensures that the trade only executes within the desired price range.
For example, if you own a stock currently trading at $100 and want to sell it if the price drops to $95 but only if you can get at least $94, you would place a stop limit order with a stop price of $95 and a limit price of $94.
How Does Stop Limit Order Work?
Understanding the Mechanics
When a stop limit order is placed, the stop price acts as a trigger. Once the market price reaches this trigger point, the order converts into a limit order. The limit order then waits for the market price to reach or exceed the specified limit price before executing the trade.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Set the stop price as your trigger point.
- Set the limit price as the minimum or maximum acceptable price for execution.
- Wait for the market price to reach the stop price.
- Once triggered, the order becomes a limit order.
- The trade executes only if the market price meets or exceeds the limit price.
Key Considerations
It’s important to note that if the market price moves too quickly past your limit price after the stop price is triggered, your order may not be executed. This risk is inherent in stop limit orders and should be considered carefully when setting your parameters.
Read also:Inside Out 2 A Financial Journey Into The Heart Of Emotions
Advantages of Stop Limit Order
Stop limit orders offer several advantages that make them appealing to traders:
- Precision: You have precise control over when and at what price your trade executes.
- Protection: They help protect your investments by setting boundaries for execution.
- Flexibility: You can tailor your orders to fit specific trading strategies.
- Cost Management: By specifying a limit price, you ensure that trades do not execute at unfavorable prices.
These benefits make stop limit orders a valuable tool for managing risk and optimizing trading outcomes.
Disadvantages of Stop Limit Order
While stop limit orders offer significant advantages, they also come with some drawbacks:
- Execution Risk: If the market price moves too quickly, your order might not execute at all.
- Complexity: Understanding and setting up stop limit orders correctly can be challenging for beginners.
- Market Gaps: In volatile markets, price gaps can occur, causing your order to miss execution.
Traders must weigh these risks against the benefits before incorporating stop limit orders into their strategies.
When to Use Stop Limit Order
Situations Where Stop Limit Orders Are Ideal
Stop limit orders are particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- When you want to protect profits on a stock that has appreciated in value.
- When you aim to buy a stock at a specific lower price during a downturn.
- When you need to set boundaries for trades in highly volatile markets.
Strategic Applications
Traders often use stop limit orders as part of a broader risk management strategy. By setting these orders strategically, they can safeguard their portfolios against sudden market movements while still maintaining control over trade execution.
Examples of Stop Limit Order in Action
Let’s explore a couple of real-world examples to illustrate how stop limit orders work:
Example 1: Selling a Stock
Suppose you own shares of Company XYZ currently trading at $50. You want to sell if the price drops to $48 but only if you can get at least $47. You place a stop limit order with a stop price of $48 and a limit price of $47. If the stock price falls to $48, the order activates and becomes a limit order. The trade will execute only if the price remains at or above $47.
Example 2: Buying a Stock
If you’re interested in buying Company ABC but only if the price drops to $30 or lower, you can place a stop limit order with a stop price of $30 and a limit price of $29. If the stock price declines to $30, the order activates, and the trade will execute if the price stays at or below $29.
Stop Limit Order vs Stop Market Order
Key Differences
While both stop limit orders and stop market orders use a stop price to trigger trades, they differ in how the trade is executed:
- Stop Limit Order: Executes only within the specified limit price range.
- Stop Market Order: Executes immediately at the best available price once triggered.
Choosing the Right Order Type
Your choice between these two order types depends on your trading goals and risk tolerance. Stop limit orders provide more control but carry execution risk, while stop market orders guarantee execution but may result in less favorable prices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Stop Limit Orders
Setting Unrealistic Prices
One common mistake is setting stop or limit prices that are too far from the current market price, making it unlikely for the order to execute.
Ignoring Market Conditions
Traders sometimes fail to account for market volatility, leading to missed executions or unfavorable outcomes.
Not Reviewing Orders Regularly
It’s essential to monitor and adjust your stop limit orders as market conditions change to ensure they remain effective.
Best Practices for Traders Using Stop Limit Orders
To maximize the effectiveness of stop limit orders, consider the following best practices:
- Set realistic and well-researched stop and limit prices.
- Monitor market trends and adjust your orders accordingly.
- Use stop limit orders as part of a comprehensive risk management strategy.
- Stay informed about market news and events that could impact your trades.
By following these guidelines, traders can harness the power of stop limit orders to enhance their trading success.
Conclusion
Stop limit orders are a valuable tool for traders seeking greater control and precision in their trading activities. By understanding their mechanics, advantages, and limitations, you can incorporate them effectively into your trading strategy. Remember to set realistic parameters, monitor market conditions, and adjust your orders as needed to achieve the best possible outcomes.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with stop limit orders in the comments below. Feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into trading and investment strategies. Happy trading!
For further reading and research, consider consulting reputable sources such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) website or financial publications like The Wall Street Journal.